Agents
Learn how to create, customize, and leverage LibreChat's AI Agents - a powerful framework for building custom AI assistants with any model provider.
Agents: Build Custom AI Assistants
LibreChat's AI Agents feature provides a flexible framework for creating custom AI assistants powered by various model providers.
This feature is similar to OpenAI's Assistants API and ChatGPT's GPTs, but with broader model support and a no-code implementation, letting you build sophisticated assistants with specialized capabilities.
Getting Started
To create a new agent, select "Agents" from the endpoint menu and open the Agent Builder panel found in the Side Panel.
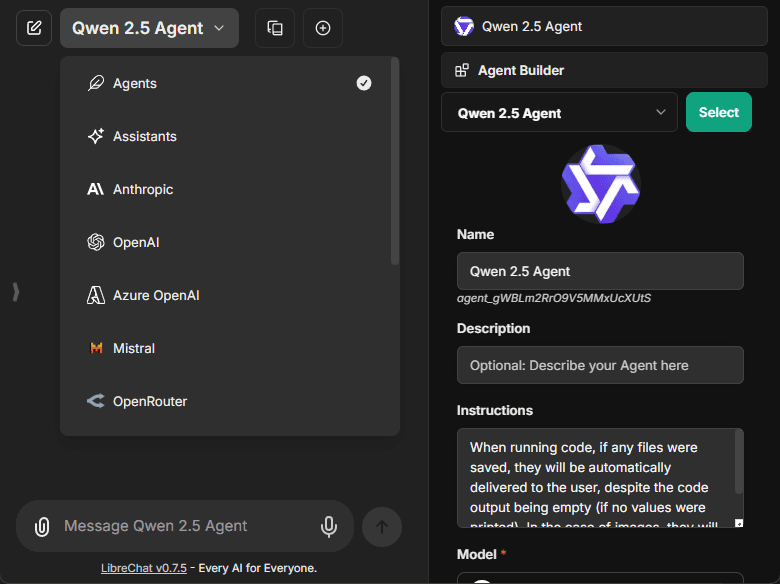
The creation form includes:
- Avatar: Upload a custom avatar to personalize your agent
- Name: Choose a distinctive name for your agent
- Description: Optional details about your agent's purpose
- Instructions: System instructions that define your agent's behavior
- Model: Select from available providers and models
Existing agents can be selected from the top dropdown of the Side Panel.
- Also by mention with "@" in the chat input.
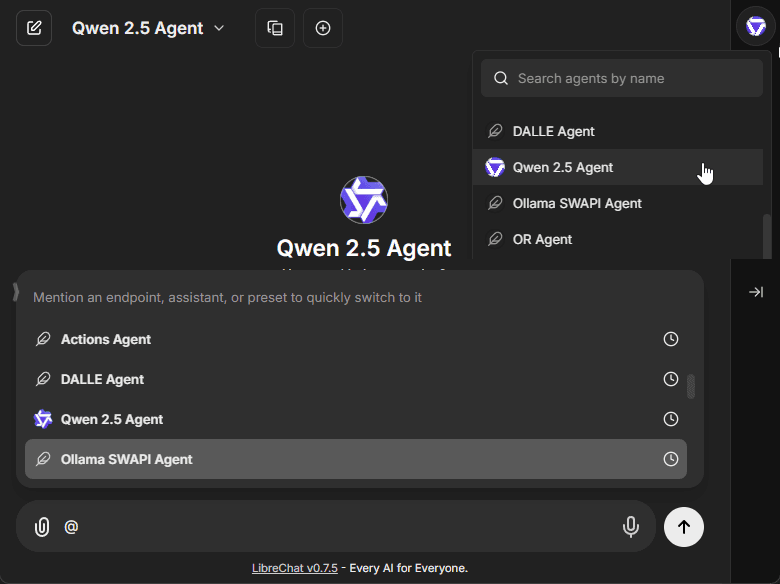
Model Configuration
The model parameters interface allows fine-tuning of your agent's responses:
- Temperature (0-1 scale for response creativity)
- Max context tokens
- Max output tokens
- Additional provider-specific settings
Agent Capabilities
Note: All capabilities can be toggled via the
librechat.yamlconfiguration file. See docs/configuration/librechat_yaml/object_structure/agents#capabilities for more information.
Code Interpreter
When enabled, the Code Interpreter capability allows your agent to:
- Execute code in multiple languages, including:
- Python, JavaScript, TypeScript, Go, C, C++, Java, PHP, Rust, and Fortran
- Process files securely through the LibreChat Code Interpreter API
- Run code without local setup, configuration, or sandbox deployment
- Handle file uploads and downloads seamlessly
- More info about the Code Interpreter API
- Requires an API Subscription from code.librechat.ai
File Search
The File Search capability enables:
- RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) functionality
- Semantic search across uploaded documents
- Context-aware responses based on file contents
- File attachment support at both agent and chat thread levels
File Context
The File Context capability allows your agent to store extracted text from files as part of its system instructions:
- Extract text while maintaining document structure and formatting
- Process complex layouts including multi-column text and mixed content
- Handle tables, equations, and other specialized content
- Work with multilingual content
- Text is stored in the agent's instructions in the database
- No OCR service required - Uses text parsing by default with fallback methods
- Enhanced by OCR - If OCR is configured, extraction quality improves for images and scanned documents
- Uses the same processing logic as "Upload as Text": OCR > STT > text parsing
- More info about OCR configuration
Note: File Context includes extracted text in the agent's system instructions. For temporary document questions in individual conversations, use Upload as Text from the chat instead.
Model Context Protocol (MCP)
MCP is an open protocol that standardizes how applications provide context to Large Language Models (LLMs), acting like a universal adapter for AI tools and data sources.
For more information, see documentation on MCP.
Agents with MCP Tools
- Configure MCP servers in your
librechat.yamlfile - Restart LibreChat to initialize the connections
- Create or edit an agent
- Click the "Add Tools" button in the Agent Builder panel to open the Tools Dialog shown below
- Select the MCP server(s) you want to add - each server appears as a single entry
- Save your changes to the agent
In this example, we've added the Spotify MCP server to an agent.
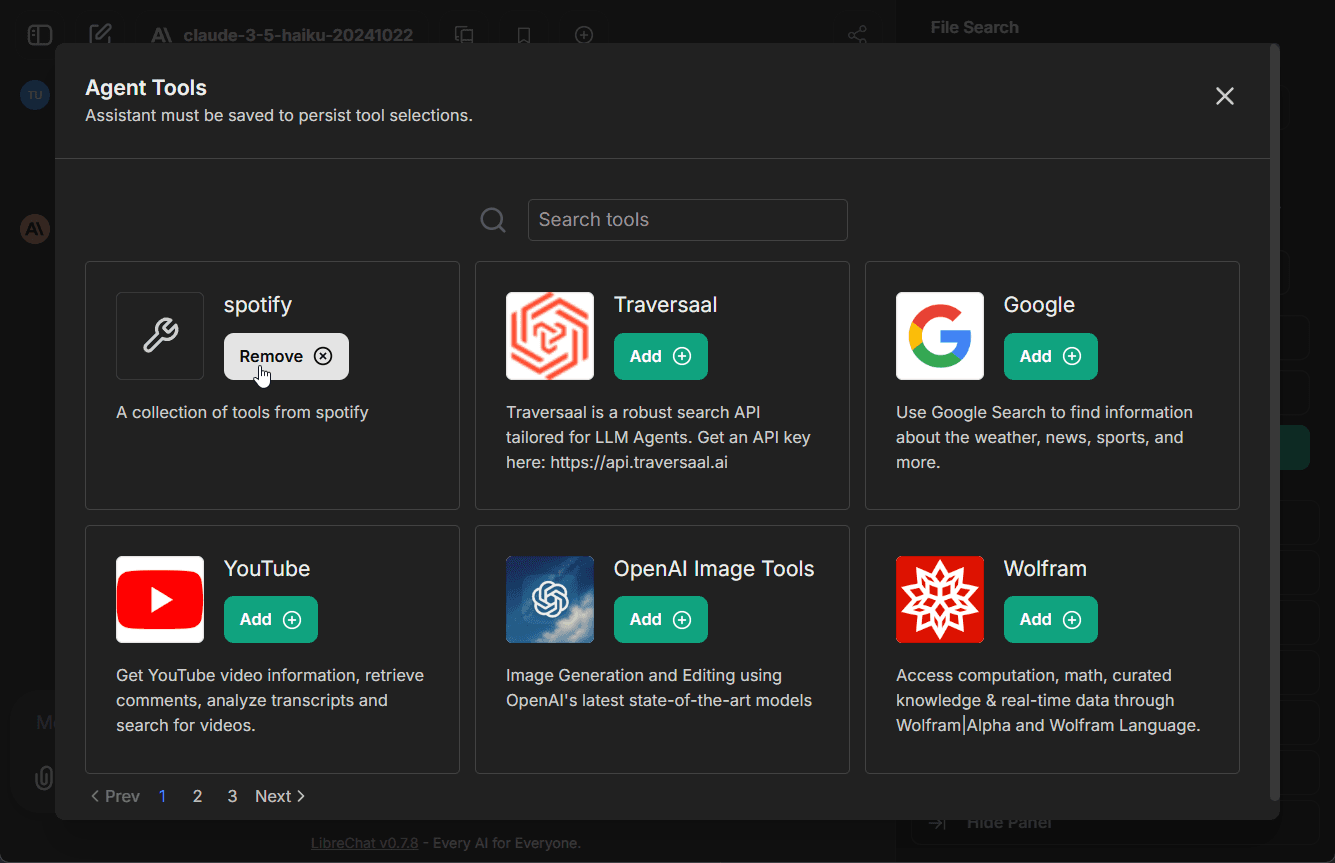
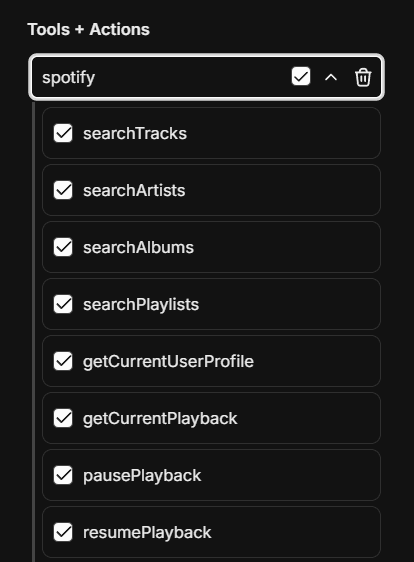
Managing MCP Tools
Once an MCP server is added to an agent, you can fine-tune which specific tools are available:
- After adding an MCP server, expand it to see all available tools
- Check/uncheck individual tools as needed
- For example, the Spotify MCP server provides ~20 tools (search, playback control, playlist management, etc.)
- This granular control lets you limit agents to only the tools they need
Learn More:
Deferred Tools
Deferred tools allow agents to have access to many MCP tools without loading them all into the LLM context upfront. Instead, deferred tools are discoverable at runtime via a Tool Search mechanism.
This is especially useful when an agent has access to many MCP servers with dozens of tools—loading them all would consume a large portion of the context window and degrade response quality.
How it works:
- Tools marked as "deferred" are excluded from the initial LLM context
- A
ToolSearchtool is automatically added, allowing the LLM to discover and load deferred tools on demand - Once discovered, the tool is available for the rest of the conversation
Configuring deferred tools:
- Open the Agent Builder and add MCP tools
- Click the dropdown on any MCP tool
- Toggle "Defer Loading" — deferred tools show a clock icon
Note: The deferred_tools capability is enabled by default. It can be toggled via the librechat.yaml agents configuration.
Artifacts
The Artifacts capability enables your agent to generate and display interactive content:
- Create React components, HTML code, and Mermaid diagrams
- Display content in a separate UI window for clarity and interaction
- Configure artifact-specific instructions at the agent level
- More info about Artifacts
When enabled, additional instructions specific to the use of artifacts are added by default. Options include:
- Enable shadcn/ui instructions: Adds instructions for using shadcn/ui components (a collection of re-usable components built using Radix UI and Tailwind CSS)
- Custom Prompt Mode: When enabled, the default artifacts system prompt will not be included, allowing you to provide your own custom instructions
Configuring artifacts at the agent level is the preferred approach, as it allows for more granular control compared to the legacy app-wide configuration.
If you enable Custom Prompt Mode, you should include at minimum the basic artifact format in your instructions.
Here's a simple example of the minimum instructions needed:
Tools
Agents can also be enhanced with various built-in tools:
-
OpenAI Image Tools: Image generation & editing using GPT-Image-1
-
DALL-E-3: Image generation from text descriptions
-
Stable Diffusion / Flux: Text-to-image generation
-
Wolfram: Computational and mathematical capabilities
-
OpenWeather: Weather data retrieval
-
Google Search: Access to web search functionality
-
Calculator: Mathematical calculations
-
Tavily Search: Advanced search API with diverse data source integration
-
Azure AI Search: Information retrieval
-
Traversaal: A robust search API for LLM Agents
-
Tools can be disabled using the
librechat.yamlconfiguration file:
Actions
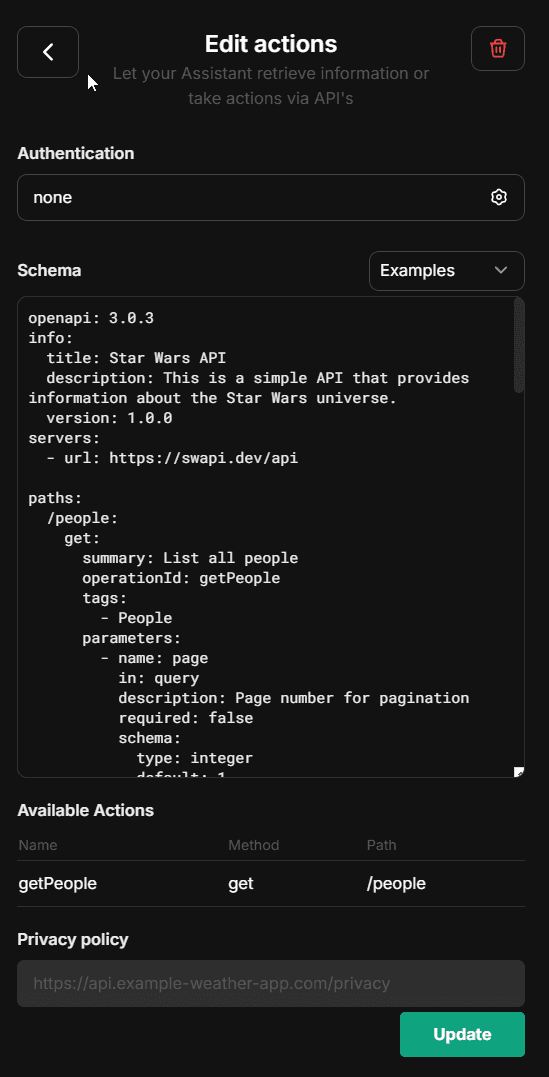
With the Actions capability, you can dynamically create tools from OpenAPI specs to add to your Agents.
Clicking the button above will open a form where you can input the OpenAPI spec URL and create an action:
- Actions can be disabled using the
librechat.yamlconfiguration file: - Individual domains can be whitelisted for agent actions:
- Note that you can add add the 'x-strict': true flag at operation-level in the OpenAPI spec for actions.
If using an OpenAI model supporting it, this will automatically generate function calls with 'strict' mode enabled.
- Strict mode supports only a partial subset of json. Read https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/structured-outputs/some-type-specific-keywords-are-not-yet-supported for details.
Agent Chain
The Agent Chain capability enables a Mixture-of-Agents (MoA) approach, allowing you to create a sequence of agents that work together:
- Create chains of specialized agents for complex tasks
- Each agent in the chain can access outputs from previous agents
- Configure the maximum number of steps for the agent chain
- Note: Access this feature from the Advanced Settings panel in the Agent Builder
- Note: This feature is currently in beta and may be subject to change
- The current maximum of agents that can be chained is 10, but this may be configurable in the future
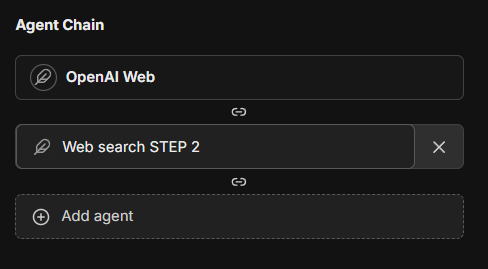
This feature introduces a layered Mixture-of-Agents architecture to LibreChat, where each agent takes all the outputs from agents in the previous layer as auxiliary information in generating its response, as described in the eponymous "Mixture-of-Agents" paper.
Advanced Settings
Advanced settings for your agent (found in the Advanced view of the Agent form) outside of "capabilities."
Max Agent Steps
This setting allows you to limit the number of steps an agent can take in a "run," which refers to the agent loop before a final response is given.
If left unconfigured, the default is 25 steps, but you can adjust this to suit your needs. For admins, you can set a global default as well as a global maximum in the librechat.yaml file.
A "step" refers to either an AI API request or a round of tool usage (1 or many tools, depending on how many tool calls the LLM provides from a single request).
A single, non-tool response is 1 step. A singular round of tool usage is usually 3 steps:
- API Request -> 2. Tool Usage (1 or many tools) -> 3. Follow-up API Request
File Management
Agents support multiple ways to work with files:
In Chat Interface
When chatting with an agent, you have four upload options:
-
Upload Images
- Uploads images for native vision model support
- Sends images directly to the model provider
-
Upload as Text (requires
contextcapability)- Extracts and includes full document content in conversation
- Uses text parsing by default; enhanced by OCR if configured
- Content exists only in current conversation
- See Upload as Text
-
Upload for File Search (requires
file_searchcapability, toggled ON)- Uses semantic search (RAG) with vector stores
- Returns relevant chunks via tool use
- Optimal for large documents/multiple files
- Sub-optimal for structured data (CSV, Excel, JSON, etc.)
-
Upload for Code Interpreter (requires
execute_codecapability, toggled ON)- Adds files to code interpreter environment
- Optimal for structured data (CSV, Excel, JSON, etc.)
- More info about Code Interpreter
In Agent Builder
When configuring an agent, you can attach files in different categories:
- Image Upload: For visual content the agent can reference
- File Search Upload: Documents for RAG capabilities
- Code Interpreter Upload: Files for code processing
- File Context: Documents with extracted text to supplement agent instructions
File Context uses the context capability and works just like "Upload as Text" - it uses text parsing by default and is enhanced by OCR when configured. Text is extracted at upload time and stored in the agent's instructions. This is ideal for giving agents persistent knowledge from documents, PDFs, code files, or images with text.
Processing priority: OCR > STT > text parsing (same as Upload as Text)
Note: The extracted text is included as part of the agent's system instructions.
Sharing and Permissions
Administrator Controls
Administrators have access to global permission settings within the agent builder UI:
- Enable/disable agent sharing across all users
- Control agent usage permissions
- Manage agent creation rights
- Configure platform-wide settings
The first account created for your instance is an administrator. If you need to add an additional administrator, you may access MongoDB and update the user's profile:
The use of agents for all users can also be disabled via config, more info.
User-Level Sharing
Individual users can:
- Share their agents with all users (if enabled)
- Control editing permissions for shared agents
- Manage access to their created agents
Notes
- Instructions, model parameters, attached files, and tools are only exposed to the user if they have editing permissions
- An agent may leak any attached data, whether instructions or files, through conversation--make sure your instructions are robust against this
- Only original authors and administrators can delete shared agents
- Agents are private to authors unless shared
Optional Configuration
LibreChat allows admins to configure the use of agents via the librechat.yaml file:
- Disable Agents for all users (including admins): more info
- Customize agent capabilities using: more info
Best Practices
- Provide clear, specific instructions for your agent
- Carefully consider which tools are necessary for your use case
- Organize files appropriately across the four upload categories
- Review permission settings before sharing agents
- Test your agent thoroughly before deploying to other users
Recap
- Select "Agents" from the endpoint dropdown menu
- Open the Agent Builder panel
- Fill out the required agent details
- Configure desired capabilities (Code Interpreter, File Search, File Context, etc.)
- Add necessary tools and files
- Set sharing permissions if desired
- Create and start using your agent
When chatting with agents, you can:
- Use "Upload as Text" to include full document content in conversations (text parsing by default, enhanced by OCR)
- Use "Upload for File Search" for semantic search over documents (requires RAG API)
- Add files to agent's "File Context" to included a file's full content as part of the agent's system instructions
Migration Required (v0.8.0-rc3+)
Important: Agent Permissions Migration Required
Starting from version v0.8.0-rc3, LibreChat uses a new Access Control List (ACL) based permission system for agents. If you're upgrading from an earlier version, you must run the agent permissions migration for existing agents to remain accessible.
What the Migration Does
The agent permissions migration transitions your agents from a simple ownership model to a sophisticated ACL-based system with multiple permission levels:
- OWNER: Full control over the agent
- EDITOR: Can view and modify the agent
- VIEWER: Read-only access to the agent
Without running this migration, existing agents will be inaccessible through the new permission-aware API endpoints.
Running the Migration
Choose the appropriate command based on your deployment method:
1. For the default docker-compose.yml (if you use docker compose up to start the app):
Preview changes (dry run):
Execute migration:
Custom batch size (for large datasets):
2. For the deploy-compose.yml (if you followed the Ubuntu Docker Guide):
Preview changes (dry run):
Execute migration:
Custom batch size (for large datasets):
3. For local development (from project root):
Preview changes (dry run):
Execute migration:
Custom batch size (for large datasets):
What Happens During Migration
- Private Agents: Remain accessible only to their creators (receive OWNER permission)
- Shared Agents: If an agent was previously shared, it will receive appropriate ACL entries as a Public Agent (shared to all users)
- System Detection: LibreChat automatically detects unmigrated agents at startup and displays a warning
You can adjust the resulting agent permissions via the Agent Builder UI.
Note
The same migration process applies to prompts. If you also have existing prompts, run the prompt permissions migration using the same commands but replace agent with prompt in the command names.
Agents API (Beta)
LibreChat agents can also be accessed programmatically via API, enabling external applications and scripts to interact with your agents using OpenAI-compatible SDKs or the Open Responses format.
See the Agents API documentation for setup and usage details.
What's next?
LibreChat Agents usher in a new era for the app where future pipelines can be streamlined via Agents for specific tasks and workflows across your experience in LibreChat.
Future updates will include:
- General improvements to the current Agent experience
- Multi-agent orchestration for complex workflows
- Ability to customize agents for various functions: titling (chat thread naming), memory management (user context/history), and prompt enhancement (input assistance/predictions)
- More tools, configurable tool parameters, dynamic tool creation.
Furthermore, the update introduces a new paradigm for LibreChat, as its underlying architecture provides a much needed refresh for the app, optimizing both the user experience and overall app performance.
To highlight one notable optimization, an AI generation of roughly 1000 tokens will transfer about 1 MB of data using traditional endpoints (at the time of writing, any endpoint option besides Agents and AWS Bedrock).
Using an agent, the same generation will transfer about about 52 kb of data, a 95% reduction in data transfer, which is that much less of a load on the server and the user's device.
AI Agents in LibreChat provide a powerful way to create specialized assistants without coding knowledge while maintaining the flexibility to work with your preferred AI models and providers.
#LibreChat #AIAssistants #NoCode #OpenSource
How is this guide?